
Returned Set is tightly linked to the underlying map.
• entrySet(): Returns a Set of EntrycontainsValue(Object value): Returns boolean value true if the specified value is present in the map else returns false.clear(): Removes all of the mappings from this map.This gets all methods of the HashMap but the below are directly from LinkedHashMap. LinkedHashMap way5 = new LinkedHashMap(75, 0.75f, false) LinkedHashMap way4 = new LinkedHashMap(50, 0.5f) LinkedHashMap wa圓 = new LinkedHashMap(way2) LinkedHashMap way2 = new LinkedHashMap(25) With the same mappings as the specified map.LinkedHashMap way1 = new LinkedHashMap() LinkedHashMap(Map m)- Constructs an insertion-ordered LinkedHashMap instance.Means access-order, false for insertion-order Instance with the specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode. LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder)- Constructs an empty LinkedHashMap.Instance with the specified initial capacity and load factor. LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)- Constructs an empty insertion-ordered LinkedHashMap.Specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75). LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity)- Constructs an empty insertion-ordered LinkedHashMap instance with the.Uses the default ordering which is insertion ordering. LinkedHashMap()- Constructs an empty LinkedHashMap instance with the default initial capacity (16) and.“Collection view” of the Map though and iterate it. LinkedHashMap does not implement Iterable interface so LinkedHashMap by itself can’t be iterated.Multiple threads and at least one of the threads modifies the map structurally, then the LinkedHashMap must be

If LinkedHashMap is accessed concurrently by LinkedHashMap in Java is not synchronized so it is not thread safe.If a value is inserted with theĭuplicate key, the previously stored value for the same key will be overwritten. In LinkedHashMap duplicate values are allowed but duplicate keys are not allowed.LinkedHashMap in Java permits multiple null values and a single null key.
One of the constructor of the LinkedHashMap givesĪn option to make it access order (from least-recently accessed to most-recently accessed element). Insertion order (the order in which keys were inserted into the map).

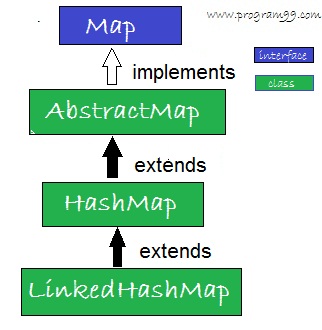
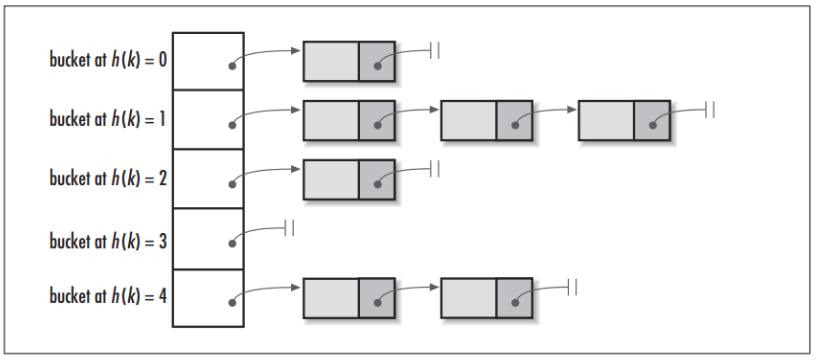
Some of the important points about LinkedHashMap in Java are. It maintains aĭoubly-linked list running through all of its entries and that's how it maintains the iteration order.Īpart from maintaining a doubly linked list the internal implementation of the LinkedHashMap is same as the LinkedHashMap in Java is a hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface. If you pass true in that constructor then access A specialĬonstructor is provided to create a LinkedHashMap that follows access ordering. Of iteration is the order in which its entries were last accessed, from least-recently accessed to most-recently.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
